Пищеварительная система
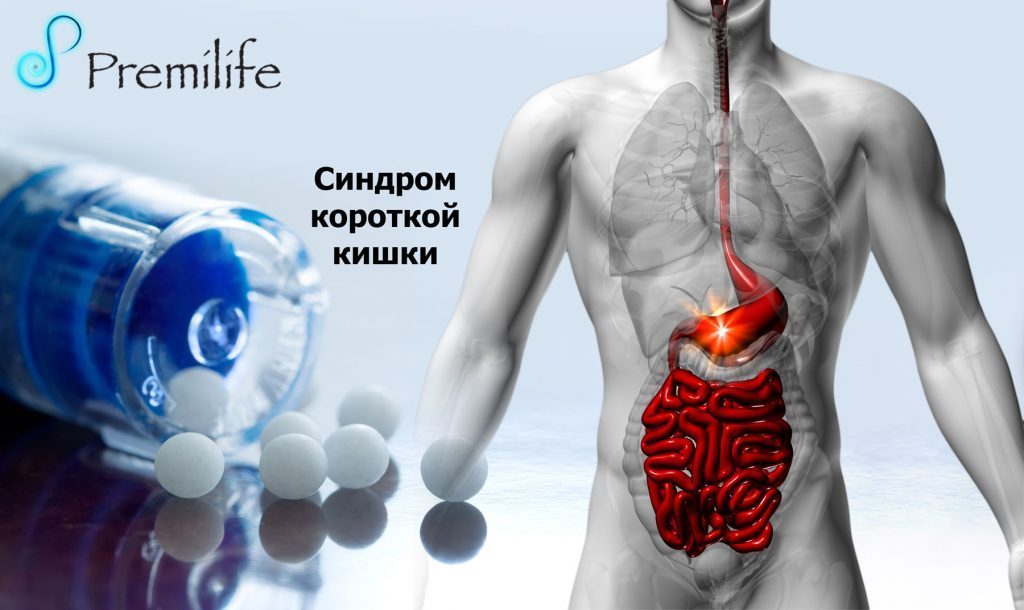
Синдром короткой кишки
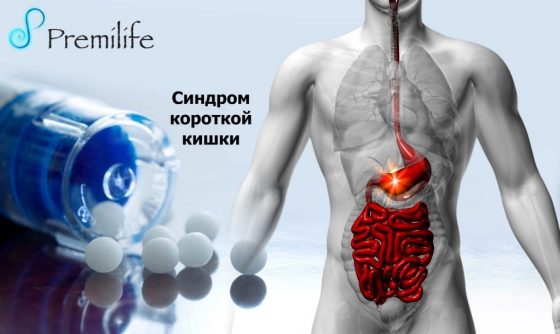
Short bowel syndrome is a condition in which nutrients are not properly absorbed (malabsorption) because a large part of the small intestine is missing or has been surgically removed.
Short bowel syndrome is a condition in which nutrients are not properly absorbed (malabsorption) because a large part of the small intestine is missing or has been surgically removed.
Causes:
When areas of the small intestine are removed by surgery, or they are missing due to a birth defect (congenital defect), there may not be enough surface area left in the remaining bowel to absorb enough nutrients from food.
This condition is likely to develop when one-half or more of the bowel is removed during surgery. Risk factors include diseases of the small intestine that may require surgery, such as Crohn’s disease. Necrotizing enterocolitis is a common cause of short bowel syndrome in infants.
Symptoms:
Diarrhea
Fatigue
Pale, greasy stools
Swelling (edema), especially of the legs
Very foul-smelling stools
Weight loss